|
|
Environmental Microbiology Technology Group
| Group Leader: |
Yang Min |
Laboratory: |
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Aquatic Chemistry |
 |
|
|
|
Environmental Microbiology Technology Group
Yang Min. MSc (1989) and Ph.D in Environmental Engineering (1992) from Hiroshima University (Japan). He worked in Organo Co. (Japan) for 6 years before moving to Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences (RCEES), Chinese Academy of Sciences. His research topics include: (1) occurrence and fates of taste/odors, DBPs and micropollutants in drinking water; (2)wastewater treatment and toxicity reduction technologies for petroleum, chemical engineering and pharmaceutical industries; system optimization and effluent safety for municipal wastewater.
Contact:E-mail: yangmin@rcees.ac.cn; Fax; Tel:10-62928390:10-62928390
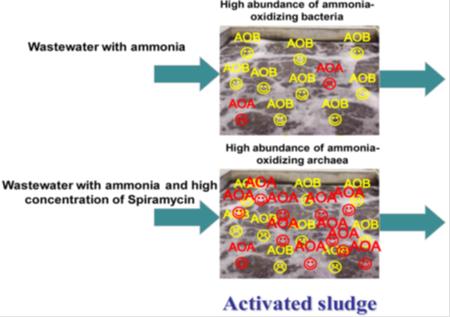
High Concentrations of the Antibiotic Spiramycin in Wastewater Lead to High
Abundance of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea in Nitrifying Populations
Yu Zhang*, Zhe Tian, Miaomiao Liu, Min Yang*
To evaluate the potential effects of antibiotics on ammonia oxidizing microbes, multiple tools including quantitative PCR (qPCR), 454-pyrosequencing, and a high-throughput functional gene array (GeoChip) were used to reveal the distribution of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and archaeal amoA (Arch-amoA) genes in three wastewater treatment systems receiving spiramycin or oxytetracycline production wastewaters. The qPCR results revealed that the copy number ratios of Arch-amoA to ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) amoA genes were the highest in the spiramycin full-scale (5.30) and pilot-scale systems (1.49 × 10?1), followed by the oxytetracycline system (4.90 × 10?4), with no Arch-amoA genes detected in the control systems treating sewage or inosine production wastewater. The pyrosequencing result showed that the relative abundance of AOA affiliated with Thaumarchaeota accounted for 78.5?99.6% of total archaea in the two spiramycin systems, which was in accordance with the qPCR results. Mantel test based on GeoChip data showed that Arch-amoA gene signal intensity correlated with the presence of spiramycin (P < 0.05). Antibiotics explained 25.8% of variations in amoA functional gene structures by variance partitioning analysis. This study revealed the selection of AOA in the presence of high concentrations of spiramycin in activated sludge systems.
References:
Zhang Y, Tian Z, Liu M, Shi ZJ, Hale L, Zhou J, Yang M. High Concentrations of the Antibiotic Spiramycin in Wastewater Lead to High Abundance of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea in Nitrifying Populations. Environ Sci Technol. 2015, 49(15): 9124-9132.
Group Leader: Prof. Min Yang

Member
|
Yu Zhang
|
Professor
|
|
Yingxin Gao
|
Associate Professor
|
|
Wei An
|
Associate Professor
|
|
Jianwei Yu
|
Associate Professor
|
|
Binghui Tian
|
Associate Professor
|
|
Rong Qi
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Haifeng Zhang
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Ming Shu
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Ze Tian
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Ran Ding
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Dongqing Zhang
|
Secretary
|
|
Lihua Xin
|
Lab manager
|
|
Hui Chen
|
Lab manager Assistant
|
|
Meng Yang
|
Lab manager Assistant
|
Postdoctoral Fellow
|
Yongzhi Chi
|
2013
|
|
Chunyan Wang
|
2013
|
|
Qin Wang
|
2013
|
|
Juan Wang
|
2015
|
|
Yuan Liu
|
2015
|
|
Ganesh
|
2015
|
|
Students
|
Degree
|
Year
|
|
Qizhen Yi
|
Ph.D
|
2011
|
|
DEV JOSHI
|
Ph.D
|
2012
|
|
Hong Zhang
|
Ph.D
|
2013
|
|
Qingyuan Guo
|
Ph.D
|
2012
|
|
Hongrui Chen
|
Ph.D
|
2012
|
|
Xin Wang
|
Ph.D
|
2012
|
|
Wenzhe Song
|
Ph.D
|
2014
|
|
Dong Chen
|
Ph.D
|
2014
|
|
Niansi Fan
|
Ph.D
|
2015
|
|
Kai Yang
|
Ph.D
|
2013
|
|
Yanhong Shi
|
Ph.D
|
2013
|
|
Zeyu Jia
|
Ph.D
|
2015
|
|
Tingting Liu
|
Ph.D
|
2015
|
|
Jiaoqi Huyan
|
Ph.D
|
2014
|
|
Yuqiong Song
|
Master
|
2013
|
|
Wei Liu
|
Master
|
2013
|
|
Luer Bao
|
Master
|
2012
|
|
Yong Yu
|
Master
|
2013
|
|
Jie Ma
|
Master
|
2013
|
|
Chunmiao Wang
|
Master
|
2014
|
|
Qiuqiu Zhang
|
Master
|
2014
|

Representative Publications:
1.Yu Zhang*, Zhe Tian, Miaomiao Liu, Zhou Jason Shi, Lauren Hale, Jizhong Zhou, Min Yang*. High Concentrations of the Antibiotic Spiramycin in Wastewater Lead to High Abundance of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea in Nitrifying Populations. Environmental Science & Technology.2015,49 (15), 9124–9132.
2.Ming Su, Jianwei Yu, Junzhi Zhang, Hui Chen, Wei An, Rolf D. Vogt, Tom Andersen, Dongmin Jia, Jingshi Wang, Min Yang. MIB-producing cyanobacteria (Planktothrix sp.) in a drinking water reservoir: Distribution and odor producing potential.Water Research.2015,68:444-453.
3.Zhe Tian, Yu Zhang*, Yuyou Li,Yongzhi Chi , Min Yang. Rapid establishment of thermophilic anaerobic microbial community during the one-step startup of thermophilic anaerobic digestion from a mesophilic digester. Water Research.2015,69:9-19.
|
|
|
|
|