The Research Group of Atmospheric Chemistry for Trace Gases
Dr. Yujing Mu is a Professor in the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences (RCEES), Chinese Academy of Sciences. He gained his B.S. at Nankai University in 1988, and his M.S. and Ph.D at RCEES in 1991 and 1997, respectively. Since July in 1997, Dr. Mu has been working in RCEES with exception the year of 1999-2000 when he was in the Centre national de la recherche scientifique(CNRS) as a post-doctor. He serves as a member of the editorial board member for the Journal Environmental Chemistry and Journal of Environmental Sciences, and member of the committee for Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences and Environmental Geology and Geochemistry Committee. So far, he has published more than 60 SCI papers, including some top journals, such as Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Journal of Geophysical Research, Journal of Chromatography A, and so on.
Research interests: the sources and sinks for atmospheric trace gases, including exchange of trace gases between the biosphere and the atmosphere; field measurements of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), H2O2, HONO and particulate matters (PMs) etc.; chemical kinetics of atmospheric VOCs and reduce sulfur compounds with radicals; emissions of pollutants from domestic coal combustion; development of online instruments for detecting the trace gases in the atmosphere.
Contact: E-mail: yjmu@rcees.ac.cn; Tel: 010-62849125; Fax: 010-62849117
High-efficiency and clean combustion technology for residential stove
Yujing Mu*, Chenglong Zhang, Junfeng Liu, Yuanyuan Zhang et al.
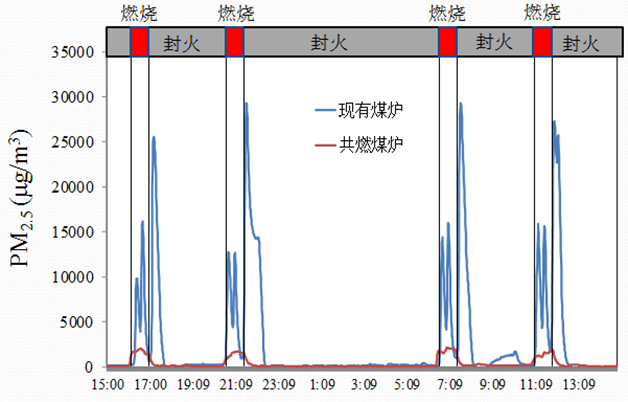
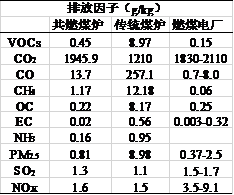
Residential coal combustion is an important source of atmospheric pollution in our country, and it has important impacts on the regional environment and human health. State and governments have carried out a series of plans to control air pollution, including promoting clean energy, using high-quality coal, and utilizing advanced stoves, but showing little effect. The widely applied traditional stoves have a very low combustion efficiency with high emission of pollution gases. For solving the aforementioned problems, we develop a high-efficiency combustion technology, named co-firing technology, which can remarkably reduce the VOC and CO emissions. Meanwhile, systematical comparisons between the co-firing and traditional stoves have been done in investigating the emission differences of air pollutants. Compared to the traditional stove, co-firing stove reduces more than 90% emission of PM2.5, CO, NH3, OC/EC and other pollutants, and the emission factors are close to those from the coal-fired power plant after dedusting. Based on the CO2 emission factor, the combustion efficiency of such co-firing stove is high up to 92%, close to that of coal-fired power plant, and 35 percent higher than the traditional stove. For the pollutants from fuel, the SO2 emission from co-firing stove is comparative to the traditional stove and power plant (after desulfurization). The NOX emission from co-firing stove is close to the traditional one, while it is far less than that from power plants. Furthermore, the new stove has been small-scale applied in Wangdu County, Hebei province, achieving many high praises. The study provides the scientific basis for developing the air pollution control measures, and it has important practical significance for improving severe haze pollution of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
Group Leader: Prof. Yujing Mu

Member
|
Junfeng Liu
|
Associate Professor
|
|
Yuanyuan Zhang
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Chenglong Zhang
|
Assistant Professor
|
|
Zhibo Zhang
|
Engineer
|
Postdoctoral Fellow
|
Name
|
Degree
|
Enter Year
|
|
Yizhen Zhou
|
Ph.D.
|
2011
|
|
Pengfei Liu
|
Ph.D.
|
2012
|
|
Chengtang Liu
|
Ph.D.
|
2012
|
|
Di Tian
|
Ph.D.
|
2012
|
|
Min Song
|
Ph.D.
|
2014
|
|
Zhuobiao Ma
|
Ph.D.
|
2015
|
|
Chaoyang Xue
|
Ph.D.
|
2014
|
|
Qianqian Du
|
Master
|
2013
|
|
Can Ye
|
Master
|
2014
|
|
Chun Chen
|
Master
|
2015
|

Representative Publications:
1. Gen Zhang, Yujing Mu*, Lingxi Zhou, Chenglong Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Junfeng Liu, Shuangxi Fang, Bo Yao. Summertime distributions of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and peroxypropionyl nitrate (PPN) in Beijing: Understanding the sources and major sink of PAN. Atmospheric Environment, 2015, 103: 289-296.
2. Ye Cheng, Chenglong Zhang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Hongxing Zhang, Xu Sun, Yujing Mu*. Characteristics and anthropogenic sources of carbonyl sulfide in Beijing. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28: 163-170.
3. Kankan Liu, Chenglong Zhang, Ye Cheng, Chengtang Liu, Hongxing Zhang, Gen Zhang, Xu Sun, Yujing Mu*. Serious BTEX pollution in rural area of the North China Plain during winter season. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 30: 186-190.
|