Catalytic Purification Group Chun Hu, Ph.D, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Environmental Aquatic Chemistry, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. She attained B.S. and M.Sc. in1985 and 1993 at Jilin University. And in 2001, She received Ph.D degree from Chinese Academy of Sciences. In 1996 and 2001, she worked as visiting scholar at German Research Center for Environmental Health, and Chinese University of Hong Kong. Then she established her group for catalytic purification of water in 2005. Major research direction: Chemistry for the control of water pollution, including safe transformation of pollutants in water, safe transportation and distribution of potable water supply. Proposing mechanism and method for the transformation of pollutants in water and the stability of water quality in drinking water distribution. By now, more than 90 publications on J. Am. Chem. Soc,Environ. Sci. & Technol and so on. Her findings about the electron transfer at water-solid interface are payed attetion by international peer, SCI publications were cited for more than 2500 times. Contact:E-mail: huchun@rcees.ac.cn;: 010-62849628;TelFax:010-62923541 The electron transfer and the enhancement of H2O2 utilization efficiency at Cu-based Fenton catalyst-pollutant -water interface. Fenton reactions have been proven to be effective methods for eliminating the many recalcitrant organic pollutants in water due to the generation of hydroxyl radicals (·OH). However, the low reaction rate and the excessive consumption of H2O2 limited the application of Fenton reactions to practical water treatment. In this present, mesoporous Cu+/2+ -doped γ-Al2O3(γ-Cu-Al2O3) was prepared. The catalyst was found to be highly effective and stable for the degradation and mineralization of aromatic pollutants, and the high utilization efficiency of H2O2 was maintained at approximately 90% prior to the disappearance of the initial aromatic pollutants. In the reaction system, in addition to the unselective oxidation of ·OH, H2O2 directly attacked the s-Cu2+-complexes aromatic ring with the phenolic OH group, which resulted in the formation of ·OH and HO-adduct radicals that were oxidized to hydroxylation products by reduction of Cu2+ in the s-Cu2+-complexes to Cu+. The process prevented Cu2+ from oxidizing H2O2 to form HO2·/O2·− or O2, which enhanced the Cu+/Cu2+ cycle, the formation of ·OH and the utilization efficiency of H2O2. Meanwhile g-C3N4-CuCo-g-Al2O3 heterogeneous Fenton catalyst was prepared. It was found that the s-Cu - C3N4 complexes were formed by the phenolic OH group of hydroxylated g-C3N4 and the surface Cu,and the ·OH was generated with the reaction of Cu+ and H2O2, the resulted Cu2+ was reduced to Cu+ by the p electron of aromatic ring of C3N4 from s-Cu2+- C3N4 complexes, meanwhile the resulted suface h+ of C3N4 reacted with H2O forming ·OH. Thus, it amounted to one H2O2 changing into 2 ·OH. Therefore, the highutilization efficiency of H2O2 was more than 90% for degradation and mineralization of bisphenol A and so on most of refractory pollutants. Our findings present new Fenton catalytic mechanism for the first time, dealing with the key problem of Fenton technology for pratical application. 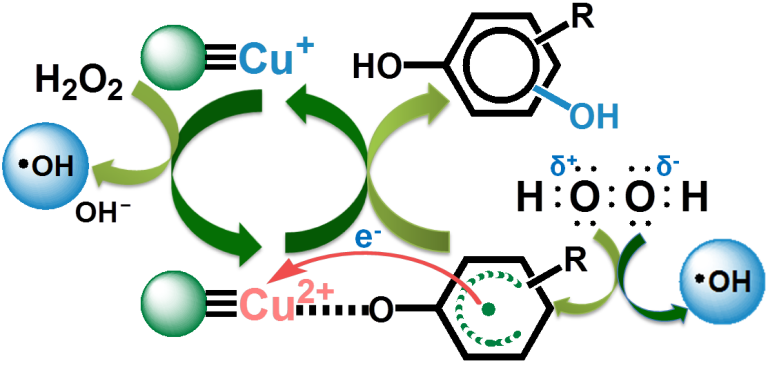 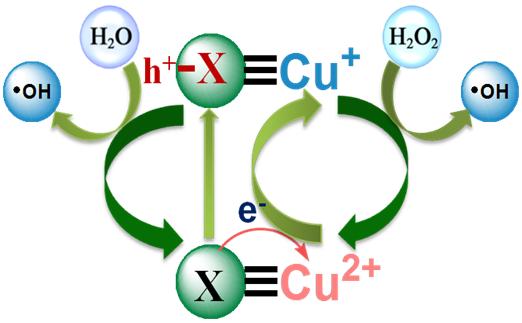
heterogeneous Fenton reaction mechanism of nano-Cu based catalyst References: 1. Lyu Lai, Zhang Lili, Wang Qiyuan, Nie Yulun, Hu Chun*. (2015) Enhanced Fenton catalytic efficiency of g-Cu-Al2O3 by s-Cu2+-Ligand Complexes from aromatic pollutant degradation, Environ. Sci. Technol., 49(14) , 8639-8647. 2. Lyu Lai., Zhang Lili., Hu Chun*. (2015) Enhanced Fenton-like degradation of pharmaceuticals over framework copper species in copper-doped mesoporous silica microspheres, Chem. Eng. J., 274, 298-306. 3. 一种固体芬顿催化剂及其制备方法与应用, 胡春, 吕来,张丽丽,发明专利受理号:201610121173.8. Group Leader: Prof. Chun Hu 
Member | Yulun Nie | Associate Professor | | Haibo Wang | Associate Professor | | Lili Zhang | Associate Professor | | Xuhua Liu | Secretary | Postdoctoral Fellow | Students | Degree | Year | | Jishuai Bing | Ph.D | 2012 | | Huanhuan Ji | Ph.D | 2013 | | Luchao Han | Ph.D | 2013 | | Lai Liu | Ph.D | 2012 | | Lizhong Liu | Ph.D | 2014 | | Xueci Xing | Ph.D | 2015 | | Fan Li | Ph.D | 2016 | | Sai Zhang | Master | 2015 | | Guangfei Yu | Master | 2016 | | Ning Jiang | Master | 2016 | | Huihui Li | Master | 2016 (joint-training) | | Qingqing Jin | Master | 2016 (joint-training) | | Yilun Shi | Master | 2016 (joint-training) | 
Representative Publications: 1. Lyu Lai, Zhang Lili, Wang Qiyuan, Nie Yulun, Hu Chun*. (2015) Enhanced Fenton catalytic efficiency of g-Cu-Al2O3 by s-Cu2+-Ligand Complexes from aromatic pollutant degradation, Environ. Sci. Technol., 49(14) , 8639-8647. 2. Bing Jishuai, Hu Chun*, Nie Yulun, Yang Min, Qu Jiuhui. (2015), Mechanism of catalytic ozonation in Fe2O3/Al2O3@SBA-15 aqueous suspension for destruction of ibuprofen, Environ. Sci. Technol., 49 1690-1697. 3. Wang Haibo, Hu Chun*, Han luchao, Yang Min. (2015) Effects of microbial cycling of Fe(II)/Fe(III) and Fe/N on cast iron corrosion in simulated drinking water distribution systems, Corros. Sci. 100, 599–606. |